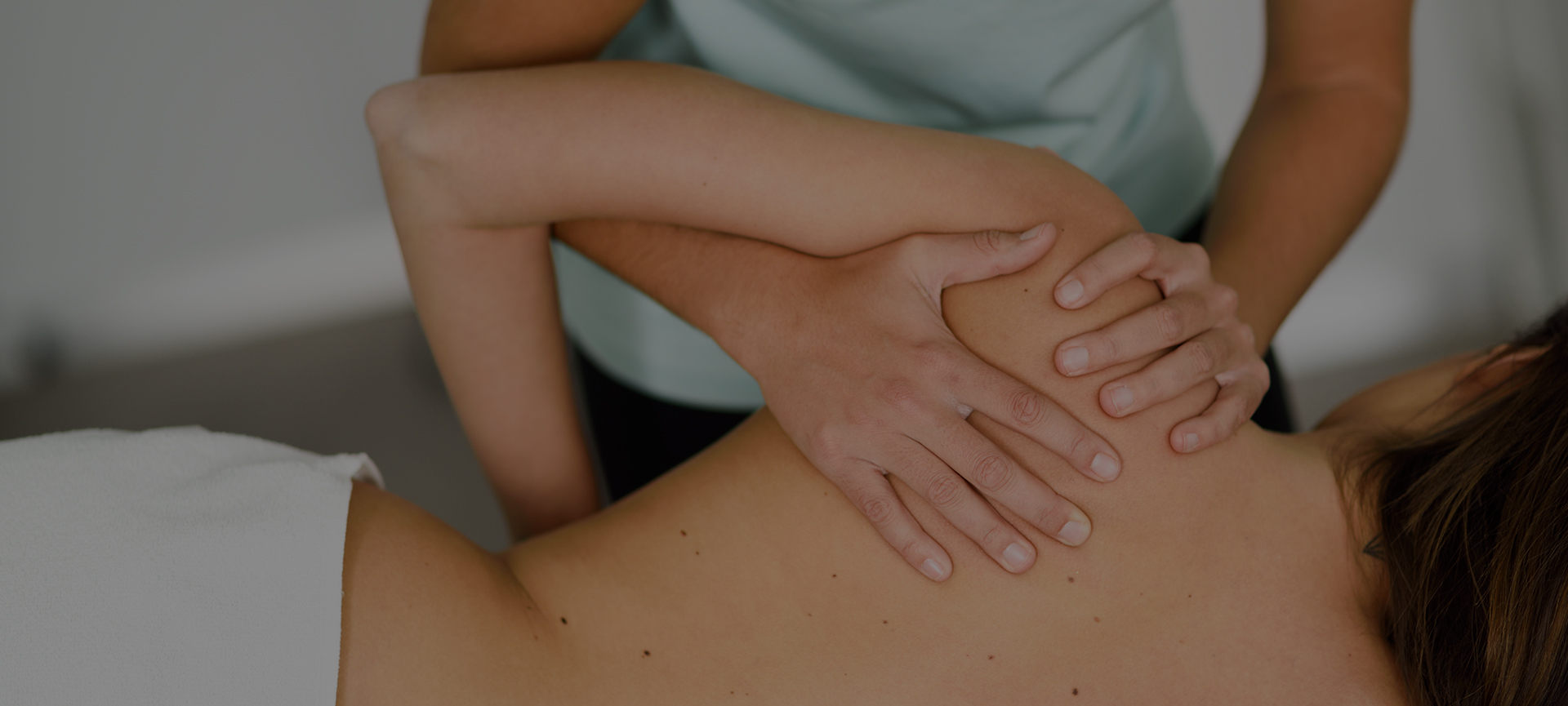
Osteopathy
Osteopathy is a system of diagnosis and treatment for a wide range of medical conditions and problems and can be helpful for babies, children, adolescents, adults, and pregnancy. It uses gentle structural and cranial techniques and concentrates on the interrelationship between the structure and function of the body. By working with the body’s muscles, bones, nerves, organs, and connective tissue, osteopathy helps to relieve and eliminate aches and pain. This therapy is classified as a ‘manual’ therapy, whereby practitioners use their hands to help treat the person’s physical or anatomical self. Osteopaths are not allowed to use the term ‘physical’ therapists as this term is protected by the Physiotherapist profession and according to the HCPC (Health and Care Professions Council), using this term would suggest we are misleading the public. In order to remain as TRANSPARENT as possible, we treat the person by treating their physical bodies.
Cranial Osteopathy
Cranial osteopathy is a branch which uses gentle techniques that help to release tension and balance the body’s tissues and different systems in order to allow the body to work at optimum level. It is used for neck pain, back pain, joint pain, pelvic pain, muscle pain, headaches, migraines, digestive problems and behavioural problems.

Western Medical Acupuncture
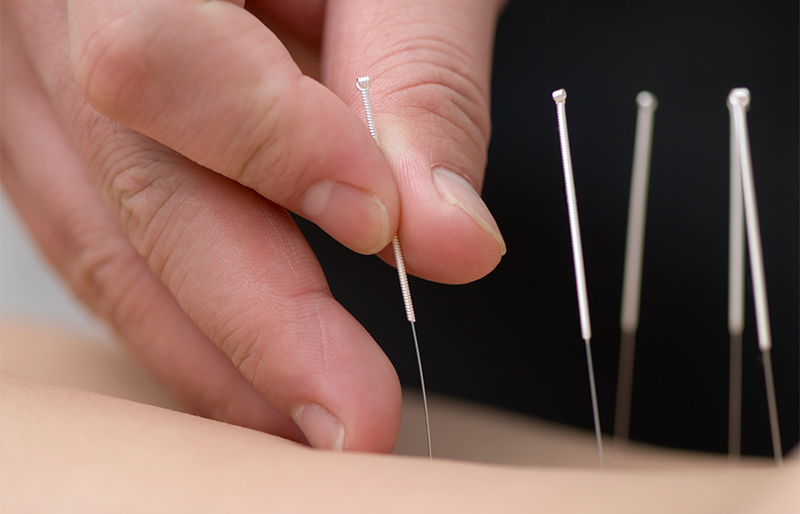
Western Medical Acupuncture is a therapeutic modality involving the insertion of fine needles. It is an adaptation of Chinese acupuncture using current knowledge of anatomy, physiology and pathology, and the principles of evidence based medicine. While Western medical acupuncture has evolved from Chinese acupuncture, its practitioners no longer adhere to concepts such as Yin/Yang and circulation of Qi, and regard acupuncture as part of conventional medicine rather than a complete alternative medical system. It is used to treat neck pain, back pain, joint pain from hands and feet, pelvic pain, muscle pain, headaches, migraines, digestive problems.

